Housing Affordability
In 2023, 79% of households were unable to afford the median-priced home, up from 72%.
Unfavorable movement since the last available data
Benchmark: The percentage of households unable to afford the median-priced home will remain below 50%.
Overview
Data on homeownership affordability shows the continuation of a troubling trend. The COVID-19 pandemic sparked a surge in homebuying. That, combined with a lack of housing stock, has increased prices across the state. The estimated percentage of households that cannot afford the median-priced home has risen from 56% in 2020 to 79% in 2023. This means the cost of the home’s mortgage, taxes, and insurance would exceed 30% of the household’s income. This number may be inflated due to an increase in sales of high-priced homes. Nevertheless, the need for affordable housing is a recurring theme across the state.
Housing is a significant portion of household budgets, and housing costs reflect everything from the supply of housing stock, to public policies regarding planning and new construction, to lending practices and interest rates. Regions with affordable housing are better able to attract and retain workers. Affordable housing also has broad positive impacts on health and childhood development, which benefit individuals and communities alike.
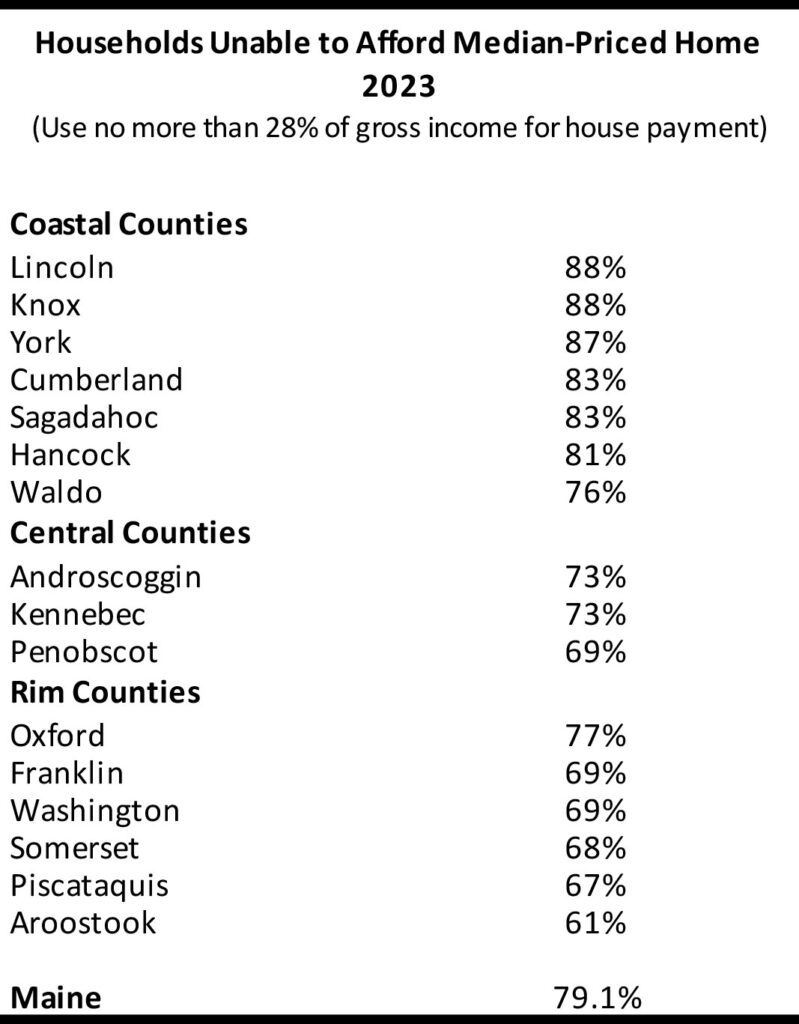
Fig. A
On mobile? Viewing this data is easier at a computer.
Maine Households Unable to Afford Median-Priced Home
Source: MaineHousing







